Warp/Transform Image | OpenCV vs Pillow | Python
This tutorial will show you how to warp/transform an image in OpenCV (cv2) and Pillow (PIL), using the perspective transformation technique.
OpenCV
h, w = cv2_img.shape[:2]
shear_x = int(round(0.5 * w))
new_w = w + shear_x
src_rect = np.array([[0, 0], [0, h], [w, h], [w, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
dst_rect = np.array([[0, 0], [shear_x, h], [new_w, h], [w, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src_rect, dst_rect)
warped_cv2_img = cv2.warpPerspective(cv2_img, M, (new_w, h))The vertices of transformation are as follows:
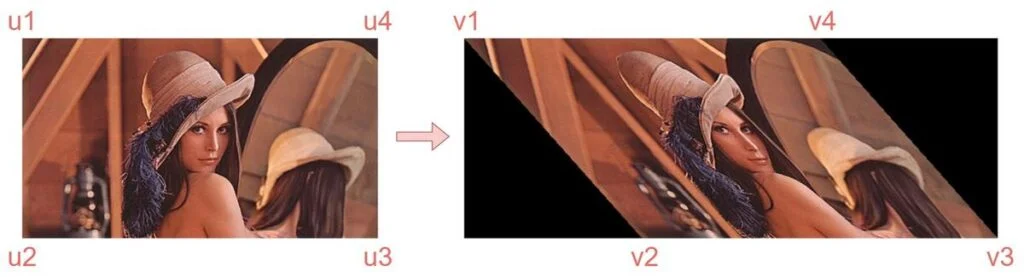
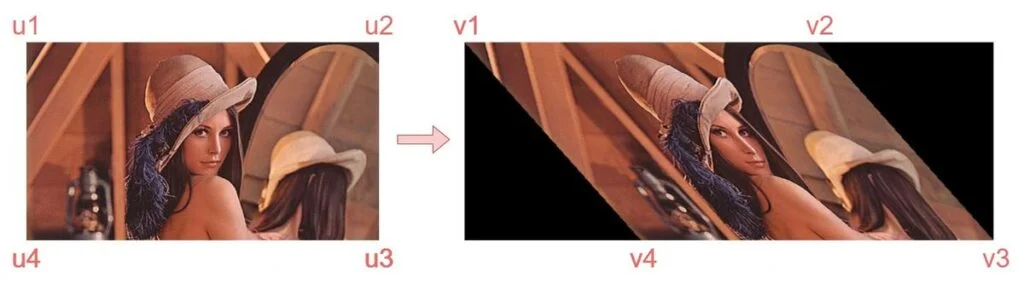
src_rect = np.array([u1, u2, u3, u4], dtype=np.float32)
dst_rect = np.array([v1, v2, v3, v4], dtype=np.float32)[u1, u2, u3, u4]:[top-left, bottom-left, bottom-right, top-right][v1, v2, v3, v4]:[top-left, bottom-left, bottom-right, top-right]
Pillow
def find_coeffs(pa, pb):
matrix = []
for p1, p2 in zip(pb, pa):
matrix.append([p1[0], p1[1], 1, 0, 0, 0,
-p2[0]*p1[0], -p2[0]*p1[1]])
matrix.append([0, 0, 0, p1[0], p1[1], 1,
-p2[1]*p1[0], -p2[1]*p1[1]])
A = np.matrix(matrix, dtype=np.float32)
B = np.array(pa).reshape(8)
res = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(A.T * A) * A.T, B)
return np.array(res).reshape(8)
w, h = pil_img.size
shear_x = int(round(0.5 * w))
new_w = w + shear_x
coeffs = find_coeffs([(0, 0), (w, 0), (w, h), (0, h)],
[(0, 0), (w, 0), (new_w, h), (shear_x, h)])
warped_pil_img = pil_img.transform((new_w, h), Image.Transform.PERSPECTIVE, coeffs, Image.Resampling.BICUBIC)Where pa is the four vertices in the current plane, and pb contains four vertices in the resulting plane. (find_coeffs function, modified from here)
coeffs = find_coeffs([u1, u2, u3, u4], [v1, v2, v3, v4])Full Example
OpenCV
import cv2
import numpy as np
# read image
cv2_img = cv2.imread("test_images/test1.jpg")
# warp the image
h, w = cv2_img.shape[:2]
shear_x = int(round(0.5 * w))
new_w = w + shear_x
src_rect = np.array([[0, 0], [0, h], [w, h], [w, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
dst_rect = np.array([[0, 0], [shear_x, h], [new_w, h], [w, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src_rect, dst_rect)
warped_cv2_img = cv2.warpPerspective(cv2_img, M, (new_w, h))
# show the image
cv2.imshow("cv2 warped image", warped_cv2_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()Pillow
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
# read image
pil_img = Image.open("test_images/test1.jpg")
# warp the image
def find_coeffs(pa, pb):
matrix = []
for p1, p2 in zip(pb, pa):
matrix.append([p1[0], p1[1], 1, 0, 0, 0,
-p2[0]*p1[0], -p2[0]*p1[1]])
matrix.append([0, 0, 0, p1[0], p1[1], 1,
-p2[1]*p1[0], -p2[1]*p1[1]])
A = np.matrix(matrix, dtype=np.float32)
B = np.array(pa).reshape(8)
res = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(A.T * A) * A.T, B)
return np.array(res).reshape(8)
w, h = pil_img.size
shear_x = int(round(0.5 * w))
new_w = w + shear_x
coeffs = find_coeffs([(0, 0), (w, 0), (w, h), (0, h)],
[(0, 0), (w, 0), (new_w, h), (shear_x, h)])
warped_pil_img = pil_img.transform((new_w, h), Image.Transform.PERSPECTIVE, coeffs, Image.Resampling.BICUBIC)
# show the image
warped_pil_img.show("pil warped image")Syntax
OpenCV
cv2.warpPerspective(src, M, dsize[, dst[, flags[, borderMode[, borderValue]]]])\texttt{dst} (x,y) = \texttt{src} \left ( \frac{M_{11} x + M_{12} y + M_{13}}{M_{31} x + M_{32} y + M_{33}} , \frac{M_{21} x + M_{22} y + M_{23}}{M_{31} x + M_{32} y + M_{33}} \right )Parameters:
src: input image.dst: output image that has the sizedsizeand the same type assrc.M: 3×3 transformation matrix.dsize: the size of the output image.flags: a combination of interpolation methods (INTER_LINEARorINTER_NEAREST) and the optional flagWARP_INVERSE_MAP, that setsMas the inverse transformation (dst→src).borderMode: pixel extrapolation method (BORDER_CONSTANTorBORDER_REPLICATE).borderValue: value used in case of a constant border; by default, it equals 0.
Returns:
- An image (Numpy array)
Pillow
Image.transform(size, method, data=None, resample=Resampling.NEAREST, fill=1, fillcolor=None)Parameters:
size: The output size in pixels, as a 2-tuple: (width, height).method: The transformation method. This is one ofTransform.EXTENT(cut out a rectangular subregion),Transform.AFFINE(affine transform),Transform.PERSPECTIVE(perspective transform),Transform.QUAD(map a quadrilateral to a rectangle), orTransform.MESH(map a number of source quadrilaterals in one operation). It may also be anImageTransformHandlerobject, or an object with a methodmethod.getdatathat returns a tuple supplying newmethodanddatavalues.See Image.transform.data: Extra data to the transformation method.resample: Optional resampling filter. It can be one ofResampling.NEAREST(use nearest-neighbor),Resampling.BILINEAR(linear interpolation in a 2×2 environment), orResampling.BICUBIC(cubic spline interpolation in a 4×4 environment). If omitted, or if the image has mode “1” or “P”, it is set toResampling.NEAREST. See Filters.- fill: If
methodis anImageTransformHandlerobject, this is one of the arguments passed to it. Otherwise, it is unused. fillcolor: Optional fill color for the area outside the transform in the output image.
Returns:
- An
Imageobject.
References
- https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/da/d54/group__imgproc__transform.html
- https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14177744/how-does-perspective-transformation-work-in-pil
- https://pyimagesearch.com/2014/05/05/building-pokedex-python-opencv-perspective-warping-step-5-6/