Resize Image & Keep Aspect Ratio | OpenCV vs Pillow | Python
This tutorial will show you how to resize an image while preserving the aspect ratio in OpenCV (cv2) and Pillow (PIL), also, how to scale it by a scale ratio and resize it by a max height and width. If you don’t care about the aspect ratio, you can follow the previous tutorial.
1. Resize Using a Scale Ratio
OpenCV
scale_ratio = 0.6
new_width = int(cv2_img.shape[1] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(cv2_img.shape[0] * scale_ratio)
new_size = (new_width, new_height)
cv2_img_resized = cv2.resize(cv2_img, new_size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)Pillow
scale_ratio = 0.6
new_width = int(pil_img.size[0] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(pil_img.size[1] * scale_ratio)
pil_img_resized = pil_img.resize((new_width, new_height))2. Resize to Fit a Maximum Size
This will resize the image to fit your maximum size. If both the max_height and max_width are larger than the original height and width, the image will be enlarged to fit the maximum size.
OpenCV
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
height, width = cv2_img.shape[:2]
scale_ratio = min(max_width/width, max_height/height)
# reuse the code of resizing by scale ratio:
new_width = int(cv2_img.shape[1] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(cv2_img.shape[0] * scale_ratio)
new_size = (new_width, new_height)
cv2_img_resized = cv2.resize(cv2_img, new_size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)Pillow
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
width, height = pil_img.size
scale_ratio = min(max_width/width, max_height/height)
# reuse the code of resizing by scale ratio:
new_width = int(pil_img.size[0] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(pil_img.size[1] * scale_ratio)
pil_img_resized = pil_img.resize((new_width, new_height))3. Shrink by a Maximum Size
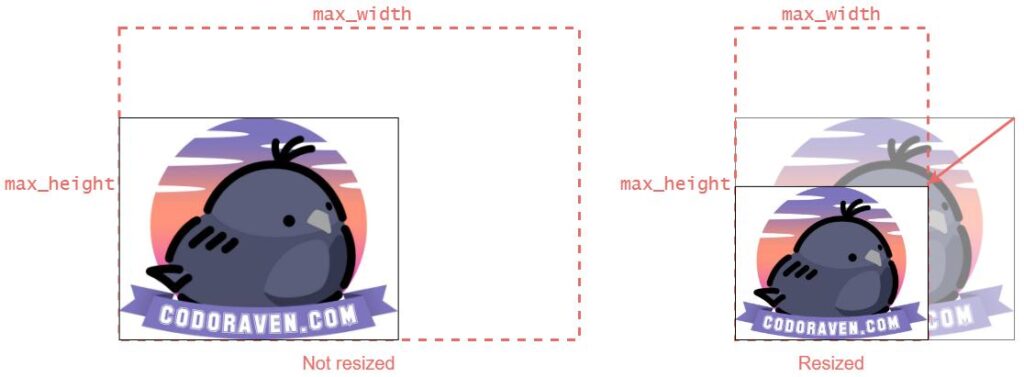
This will shrink the image if the maximum size is smaller than the original size. If both the max_height and max_width are larger than the original height and width, the image will NOT be resized.
OpenCV
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
height, width = cv2_img.shape[:2]
scale_ratio = min(max_width/width, max_height/height, 1) # use min(..., 1) to disallow enlargement
# reuse the code of resizing by scale ratio:
new_width = int(cv2_img.shape[1] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(cv2_img.shape[0] * scale_ratio)
new_size = (new_width, new_height)
cv2_img_thumbnail = cv2.resize(cv2_img, new_size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)Pillow
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
pil_img.thumbnail((max_width, max_height), Image.ANTIALIAS)Full Example
OpenCV
import cv2
# read image
cv2_img = cv2.imread("test_images/test1.jpg")
# 1. resize by scale ratio
scale_ratio = 0.6
new_width = int(cv2_img.shape[1] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(cv2_img.shape[0] * scale_ratio)
new_size = (new_width, new_height)
cv2_img_resized_1 = cv2.resize(cv2_img, new_size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
# 2. resize to fit a max size
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
height, width = cv2_img.shape[:2]
scale_ratio = min(max_width/width, max_height/height)
# reuse the code of resizing by scale ratio:
new_width = int(cv2_img.shape[1] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(cv2_img.shape[0] * scale_ratio)
new_size = (new_width, new_height)
cv2_img_resized_2 = cv2.resize(cv2_img, new_size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
# 3. shrink by max size
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
height, width = cv2_img.shape[:2]
scale_ratio = min(max_width/width, max_height/height, 1) # use min(..., 1) to disallow enlargement
# reuse the code of resizing by scale ratio:
new_width = int(cv2_img.shape[1] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(cv2_img.shape[0] * scale_ratio)
new_size = (new_width, new_height)
cv2_img_thumbnail = cv2.resize(cv2_img, new_size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
# print the old and new shape
print(f"old shape: {cv2_img.shape}")
print(f"resized by ratio shape: {cv2_img_resized_1.shape}")
print(f"resized by max size shape: {cv2_img_resized_2.shape}")
print(f"thumbnail shape: {cv2_img_thumbnail.shape}")Pillow
from PIL import Image
# read image
pil_img = Image.open("test_images/test1.jpg")
old_size = pil_img.size
# 1. resize by scale ratio
scale_ratio = 0.6
new_width = int(pil_img.size[0] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(pil_img.size[1] * scale_ratio)
pil_img_resized_1 = pil_img.resize((new_width, new_height))
# 2. resize to fit a max size
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
width, height = pil_img.size
scale_ratio = min(max_width/width, max_height/height)
# reuse the code of resizing by scale ratio:
new_width = int(pil_img.size[0] * scale_ratio)
new_height = int(pil_img.size[1] * scale_ratio)
pil_img_resized_2 = pil_img.resize((new_width, new_height))
# 3. shrink by max size
max_width = 256
max_height = 256
pil_img.thumbnail((max_width, max_height), Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
# print the old and new size
print(f"old size: {old_size}")
print(f"resized size (by scale ratio): {pil_img_resized_1.size}")
print(f"resized size (by max size): {pil_img_resized_2.size}")
print(f"thumbnail size: {pil_img.size}")Syntax
For the syntax of cv2.resize() and PIL.Image.resize() , please see the previous tutorial: Python | Resize Image | OpenCV vs Pillow.
Pillow
Image.thumbnail(size, resample=Resampling.BICUBIC, reducing_gap=2.0)Make this image into a thumbnail. This method modifies the image to contain a thumbnail version of itself, no larger than the given size.
Parameters:
size: The requested size in pixels, as a 2-tuple:(width, height).
resample: Optional resampling filter. This can be one ofResampling.NEAREST,Resampling.BOX,Resampling.BILINEAR,Resampling.HAMMING,Resampling.BICUBICorResampling.LANCZOS. If omitted, it defaults toResampling.BICUBIC. (wasResampling.NEARESTprior to version 2.5.0). See Filters.
reducing_gap: Apply optimization by resizing the image in two steps. First, reducing the image by integer times usingreduce()ordraft()for JPEG images. Second, resizing using regular resampling. The last step changes size no less than byreducing_gaptimes.reducing_gapmay be None (no first step is performed) or should be greater than 1.0. The biggerreducing_gap, the closer the result to the fair resampling. The smallerreducing_gap, the faster resizing. Withreducing_gapgreater or equal to 3.0, the result is indistinguishable from fair resampling in most cases. The default value is 2.0 (very close to fair resampling while still being faster in many cases).
Returns:
None